原生 Pytorch 和 Python 提供的 API 操作无法进行非平行计算,例如:For each batch, do an operation that depends on the data length (s.g. volume rendering)
可化简的大量的串列计算,例如:x = f 1 ( x ) , x = f 2 ( x ) , … , f = f n ( x ) x = f_1(x), x = f_2(x),\dots, f = f_n(x) x = f 1 ( x ) , x = f 2 ( x ) , … , f = f n ( x ) f 1 , f 2 , … , f n f_1,f_2,\dots,f_n f 1 , f 2 , … , f n
在 Python 中调用 cuda 需要通过 cpp 进行连接作用,调用的顺序为:
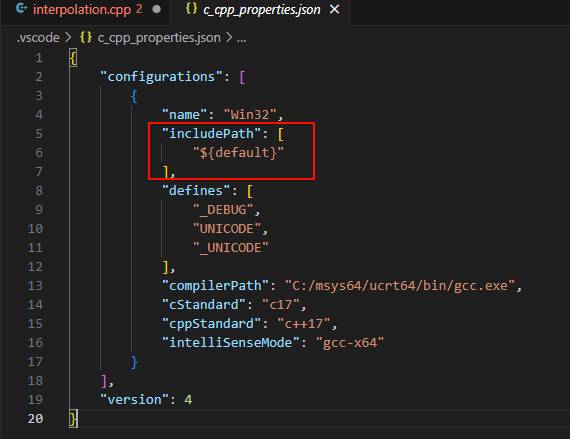
引入了PyTorch C扩展所需的头文件,该头文件包含了PyTorch的所有C API。但是这个导入如果不在 vscode 内部配置路径的话, vscode 会报错 include 错误,我们需要编辑 c_cpp_properties.json 文件,修改下面 includePath:
加入:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "D:/software/miniconda/envs/cppcuda/include" , "D:/software/miniconda/envs/cppcuda/Lib/site-packages/torch/include" , "D:/software/miniconda/envs/cppcuda/Lib/site-packages/torch/include/torch/csrc/api/include/torch" "/home/XXX/miniconda3/envs/py37/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/include/" , "/home/XXX/miniconda3/envs/py37/lib/python3.7/site-packages/torch/include/torch/csrc/api/include/" , "/home/XXX/miniconda3/envs/py37/include/python3.7m"
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 ├── ops
demo结构如上,其中
ops/src/是 Cuda/C++ 代码setup.py是编译算子的配置文件ops/ops_py/是用PyTorch包装的算子函数test_ops.py 是调用算子的测试文件
对于一个算子实现,需要用到 .cu (Cuda) 编写核函数、.cpp (C++) 编写包装函数并调用PYBIND11_MODULE 对算子进行封装。我们下面用两个 Tensor 相加的算子为例(参考https://github.com/YuxueYang1204/CudaDemo)
注意:Cuda文件和Cpp文件不能同名!!!否则编译不通过!!!
我们这里以src/sum_two_arrays/为例进行解释
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <cstdio> #define THREADS_PER_BLOCK 256 #define WARP_SIZE 32 #define DIVUP(m, n) ((m + n - 1) / n) __global__ void two_sum_kernel (const float * a, const float * b, float * c, int n) {int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;if (idx < n){void two_sum_launcher (const float * a, const float * b, float * c, int n) dim3 blockSize (DIVUP(n, THREADS_PER_BLOCK)) ;dim3 threadSize (THREADS_PER_BLOCK) ;
这里的关键是two_sum_kernel这一核函数实现数组相加功能。下面的two_sum_launcher函数负责分配线程块并调用核函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 #include <torch/extension.h> #include <torch/serialize/tensor.h> #define CHECK_CUDA(x) \ TORCH_CHECK(x.type().is_cuda(), #x, " must be a CUDAtensor " ) #define CHECK_CONTIGUOUS(x) \ TORCH_CHECK(x.is_contiguous(), #x, " must be contiguous " ) #define CHECK_INPUT(x) \ CHECK_CUDA(x); \ CHECK_CONTIGUOUS(x) void two_sum_launcher (const float * a, const float * b, float * c, int n) void two_sum_gpu (at::Tensor a_tensor, at::Tensor b_tensor, at::Tensor c_tensor) CHECK_INPUT (a_tensor);CHECK_INPUT (b_tensor);CHECK_INPUT (c_tensor);const float * a = a_tensor.data_ptr <float >();const float * b = b_tensor.data_ptr <float >();float * c = c_tensor.data_ptr <float >();int n = a_tensor.size (0 );two_sum_launcher (a, b, c, n);PYBIND11_MODULE (TORCH_EXTENSION_NAME, m) {def ("forward" , &two_sum_gpu, "sum two arrays (CUDA)" );
在 C++ 文件中实现算子的封装,文件开头的宏定义函数是为了保证传入的向量在 cuda 上(CHECK_CUDA)、传入的向量中元素地址连续(CHECK_CONTIGUOUS)。two_sum_launcher是对 cuda 文件中的声明
two_sum_gpu是与 Python 的接口,传入的参数是 PyTorch 中的 Tensor。在这一部分需要对 Tensor 做 CHECK 检验(可选),并通过.data_ptr得到 Tensor 变量的指针。对于 Tensor 在 C++ 中的使用可查阅Library API — PyTorch main documentation
最后PYBIND11_MODULE的作用是对整个算子进行封装,能够通过Python调用C++函数[3] 。对于自定义的其他算子,只用改动m.def()中的三个参数
"forward":算子的方法名,假如算子的整个模块命名为sum_double,则在Python中通过sum_double.forward调用该算子&two_sum_gpu:进行绑定的函数,这里根据自己实现的不同函数进行更改"sum two arrays (CUDA)":算子注释,在Python端调用help(sum_double.forward) 时会出现
setup.py 的写法在整个项目的根目录新建setup.py文件配置编译信息,利用setuptools对算子打包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 from setuptools import find_packages, setupfrom torch.utils.cpp_extension import BuildExtension, CUDAExtension'CudaDemo' ,'0.1.0' ,'xxx' ,'sum_single' , './ops/src/reduce_sum/sum.cpp' ,'./ops/src/reduce_sum/sum_cuda.cu' ,]'sum_double' ,'./ops/src/sum_two_arrays/two_sum.cpp' ,'./ops/src/sum_two_arrays/two_sum_cuda.cu' ,]'build_ext' : BuildExtension
文件中需要进行改动的有
name:包名version:包版本号author:作者名称ext_modules:编译C/C扩展,list 类型,每个元素为一个模块的相关信息(这里的模块在讲 Cuda/C 这一块的末尾有提到,一个模块可以含有多个具体的算子)
在ext_modules中采用CUDAExtension指明 Cuda/C++ 的文件路径 ,其中第一个参数为对应模块的名字,第二个参数为包含所有文件路径的列表
**这里的模块名和Cuda/C++中m.def()定义的算子名共同决定了调用算子的方式。**例如两数组相加的模块名是sum_double、算子方法名是forward, 所以在Python中调用该算子的方式为sum_double.forward()。
为了让自定义算子能够正常正向传播、反向传播,我们需要继承torch.autograd.Function进行算子包装。 这里以sum_double为例进行介绍
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import torchfrom torch.autograd import Functionimport sum_doubleclass SumDouble (Function ): @staticmethod def forward (ctx, array1, array2 ):"""sum_double function forward. Args: array1 (torch.Tensor): [n,] array2 (torch.Tensor): [n,] Returns: ans (torch.Tensor): [n,] """ float ()float ()return ans @staticmethod def backward (ctx, g_out ):return g_in1, g_in2
__init__.py 为了在外部调用包装好的PyTorch函数,通过ops/ops_py/__init__.py声明
1 2 from .sum import sum_single_op, sum_double_op'sum_single_op' , 'sum_double_op' ]
ops/__init__.py中